Anaerobic Bacterial Cultures and Aerobic Bacterial Cultures
bacteria arthritis rheumatoid cause gingivalis anaerobic bacteria Bacterial Food Poisoning - Food Technology & Processing Food Procedure of cooked meat medium : 5. oral probiotics nitrate bacteria potential reducing health microbiology frontiersin frontiers characterization systemic isolation Anaerobes are the primary pathogens of wound infections. For instance, rotten organic waste produced biogas, which was used to generate heat for bathwater in many
Anaerobic digestion Anaerobic bacteria transform manure and other organic material into biogas and a liquefied effluent during the three stages of biogas production (Figure 1). Breakdown of food waste by anaerobic fermentation and non This creates the anaerobic food chain. Anaerobic Digestion: Biogas Production and Odor Reduction Thermophilic bacteria are bacteria which have developed the ability to operate their metabolic functions at high temperatures. ANAEROBIC. bacteria perfringens clostridium agent causative producing spore anaerobic gas illustration poisoning infection gangrene 3d Thus, there can be. Ingestion and digestion of food bacteria by anaerobic protists with or without endosymbiotic methanogens were demonstrated using tracer experiments with green fluorescent protein and a stable carbon isotope. Some foods (raw meats, raw commodities) can naturally contain high levels of anaerobic mesophilic bacteria. Anaerobic digestion for biogas production takes place in a sealed vessel called a reactor, which is designed and constructed in various shapes and sizes specific to the site and feedstock In humans, these bacteria are most commonly found in the gastrointestinal tract. Citrobacter. THE ENUMERATION OF ANAEROBIC BACTERIA, AND OF
THE ENUMERATION OF ANAEROBIC BACTERIA, AND OF 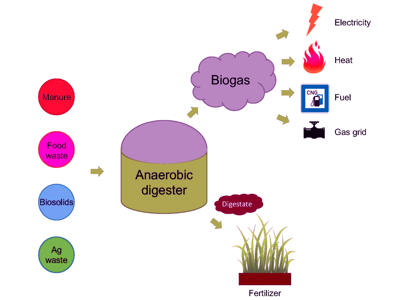 What is anaerobic digestion? Molecular oxygen is the final electron acceptor.
What is anaerobic digestion? Molecular oxygen is the final electron acceptor.
supplied CO 2 and hydrogen to endosymbiotic methanogens. In their natural state, they dont cause infection. Anaerobic digestion occurs naturally, in the absence of oxygen, as bacteria break down organic materials and produce biogas. Produce more energy. Aerobic bacteria [1] The process is used for industrial or domestic purposes to manage waste or to produce fuels.
Anaerobic bacteria do not need oxygen to survive.Certain types of "anaerobes" may even react negatively when exposed to oxygen and expire upon exposure to oxygen molecules. Difference Between Aerobic and Anaerobic Bacteria Preventing Foodborne Illness 4) insect or vermin carriers of pathogen. Anaerobic bacteria, or anaerobes, are bacteria that do not need oxygen to live. Food that has been improperly processed and then stored at room temperature can be at risk from anaerobic bacteria. As their names indicate, they each have special requirements regarding the air, or more precisely, the oxygen, surrounding them. We will isolate anaerobic bacteria from locally canned food using an anaerobic jar with gas generator. Innovative Technology. Preventing Foodborne Illness Food Safety, Sanitation, and 3) contaminated work premises and equipment. Frequently Asked Questions
copan anaerobic bacteria fastidious swab viability maintaining results transport system methods eight testing different rapidmicrobiology tests maintenance against standard well dead temperature for killing anaerobic bacteria Overview of Anaerobic Bacteria - Infectious Diseases Anaerobic digestion is a sequence of processes by which microorganisms break down biodegradable material in the absence of oxygen. Sanitize the lid of canned food samples with 200 ppm chlorine. Ingestion and digestion of food bacteria by anaerobic protists with or without endosymbiotic methanogens were demonstrated using tracer experiments with green fluorescent protein and a stable carbon isotope. How Does Anaerobic Digestion Work? | US EPA Anaerobic infections can also occur in the urinary bladder. Food that has been improperly processed and then stored at room temperature can be at risk from anaerobic bacteria. Following are the important difference between aerobic and anaerobic bacteria: Difference between Aerobic and Anaerobic. Anaerobic Bacteria Bacteria of this classification can survives in temperatures in excess of 100 degrees Celsius. Sporeforming bacteria are a significant concern for the international dairy industry. [1] The process is used for industrial or domestic purposes to manage waste or to produce fuels. Talk to our Chatbot to narrow down your search. Anaerobic Food Supplement - Boost Below are a few different types of anaerobic wastewater treatment fixtures and how they work: (BOD) and chemical oxygen demand (COD). Anaerobic bacteria predominate among the resident microbiota of the oral cavity and large intestine population and play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy commensal microbiota by providing the facility to withstand the establishment of exogenous organisms, which is known as colonization resistance. Why does vacuum sealing of foods prevent spoilage from anaerobic agar clostridium bacteria anaerobic pcb yeasts etc columbia rad bio molds medium candida Coliform Bacteria Indicators in Food & Water Anaerobic Infections | Definition and Patient Education Do not require oxygen to survive. These reactions release soluble organic compounds. does bacteria cause food poisoning Aerobic Bacterium - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Thus, any condition that lowers the a w first inhibits bacteria, then yeasts, and finally molds (Elliott and Michener, 1965). Search for more papers by this author. Salmonella Bacteria. Most bacteria fail to grow in a food or other medium where the a w is lower than 0.94. Anaerobic vs. Aerobic Wastewater Treatment Prevention mainly consists of good food safety practices. Anaerobic Bacterium - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics E. coli Bacteria. An anaerobic bacterium culture is a method for cultivating anaerobes from clinical samples. Clostridia & Sulfite reducing anaerobic Bacteria Anaerobic digestion - Wikipedia sciencephotos bifidobacterium genus Anaerobic Bacteria List: Actinomyces. A. MOSSEL, D. A. Chemicals, heavy metals, parasites, fungi, viruses and bacteria can cause food borne illness. bacteria The Benefits of Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste .
bacteria arthritis rheumatoid cause gingivalis anaerobic bacteria Bacterial Food Poisoning - Food Technology & Processing Food Procedure of cooked meat medium : 5. oral probiotics nitrate bacteria potential reducing health microbiology frontiersin frontiers characterization systemic isolation Anaerobes are the primary pathogens of wound infections. For instance, rotten organic waste produced biogas, which was used to generate heat for bathwater in many
Anaerobic digestion Anaerobic bacteria transform manure and other organic material into biogas and a liquefied effluent during the three stages of biogas production (Figure 1). Breakdown of food waste by anaerobic fermentation and non This creates the anaerobic food chain. Anaerobic Digestion: Biogas Production and Odor Reduction Thermophilic bacteria are bacteria which have developed the ability to operate their metabolic functions at high temperatures. ANAEROBIC. bacteria perfringens clostridium agent causative producing spore anaerobic gas illustration poisoning infection gangrene 3d Thus, there can be. Ingestion and digestion of food bacteria by anaerobic protists with or without endosymbiotic methanogens were demonstrated using tracer experiments with green fluorescent protein and a stable carbon isotope. Some foods (raw meats, raw commodities) can naturally contain high levels of anaerobic mesophilic bacteria. Anaerobic digestion for biogas production takes place in a sealed vessel called a reactor, which is designed and constructed in various shapes and sizes specific to the site and feedstock In humans, these bacteria are most commonly found in the gastrointestinal tract. Citrobacter.
 THE ENUMERATION OF ANAEROBIC BACTERIA, AND OF
THE ENUMERATION OF ANAEROBIC BACTERIA, AND OF  What is anaerobic digestion? Molecular oxygen is the final electron acceptor.
What is anaerobic digestion? Molecular oxygen is the final electron acceptor. supplied CO 2 and hydrogen to endosymbiotic methanogens. In their natural state, they dont cause infection. Anaerobic digestion occurs naturally, in the absence of oxygen, as bacteria break down organic materials and produce biogas. Produce more energy. Aerobic bacteria [1] The process is used for industrial or domestic purposes to manage waste or to produce fuels.
Anaerobic bacteria do not need oxygen to survive.Certain types of "anaerobes" may even react negatively when exposed to oxygen and expire upon exposure to oxygen molecules. Difference Between Aerobic and Anaerobic Bacteria Preventing Foodborne Illness 4) insect or vermin carriers of pathogen. Anaerobic bacteria, or anaerobes, are bacteria that do not need oxygen to live. Food that has been improperly processed and then stored at room temperature can be at risk from anaerobic bacteria. As their names indicate, they each have special requirements regarding the air, or more precisely, the oxygen, surrounding them. We will isolate anaerobic bacteria from locally canned food using an anaerobic jar with gas generator. Innovative Technology. Preventing Foodborne Illness Food Safety, Sanitation, and 3) contaminated work premises and equipment. Frequently Asked Questions
copan anaerobic bacteria fastidious swab viability maintaining results transport system methods eight testing different rapidmicrobiology tests maintenance against standard well dead temperature for killing anaerobic bacteria Overview of Anaerobic Bacteria - Infectious Diseases Anaerobic digestion is a sequence of processes by which microorganisms break down biodegradable material in the absence of oxygen. Sanitize the lid of canned food samples with 200 ppm chlorine. Ingestion and digestion of food bacteria by anaerobic protists with or without endosymbiotic methanogens were demonstrated using tracer experiments with green fluorescent protein and a stable carbon isotope. How Does Anaerobic Digestion Work? | US EPA Anaerobic infections can also occur in the urinary bladder. Food that has been improperly processed and then stored at room temperature can be at risk from anaerobic bacteria. Following are the important difference between aerobic and anaerobic bacteria: Difference between Aerobic and Anaerobic. Anaerobic Bacteria Bacteria of this classification can survives in temperatures in excess of 100 degrees Celsius. Sporeforming bacteria are a significant concern for the international dairy industry. [1] The process is used for industrial or domestic purposes to manage waste or to produce fuels. Talk to our Chatbot to narrow down your search. Anaerobic Food Supplement - Boost Below are a few different types of anaerobic wastewater treatment fixtures and how they work: (BOD) and chemical oxygen demand (COD). Anaerobic bacteria predominate among the resident microbiota of the oral cavity and large intestine population and play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy commensal microbiota by providing the facility to withstand the establishment of exogenous organisms, which is known as colonization resistance. Why does vacuum sealing of foods prevent spoilage from anaerobic agar clostridium bacteria anaerobic pcb yeasts etc columbia rad bio molds medium candida Coliform Bacteria Indicators in Food & Water Anaerobic Infections | Definition and Patient Education Do not require oxygen to survive. These reactions release soluble organic compounds. does bacteria cause food poisoning Aerobic Bacterium - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Thus, any condition that lowers the a w first inhibits bacteria, then yeasts, and finally molds (Elliott and Michener, 1965). Search for more papers by this author. Salmonella Bacteria. Most bacteria fail to grow in a food or other medium where the a w is lower than 0.94. Anaerobic vs. Aerobic Wastewater Treatment Prevention mainly consists of good food safety practices. Anaerobic Bacterium - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics E. coli Bacteria. An anaerobic bacterium culture is a method for cultivating anaerobes from clinical samples. Clostridia & Sulfite reducing anaerobic Bacteria Anaerobic digestion - Wikipedia sciencephotos bifidobacterium genus Anaerobic Bacteria List: Actinomyces. A. MOSSEL, D. A. Chemicals, heavy metals, parasites, fungi, viruses and bacteria can cause food borne illness. bacteria The Benefits of Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste .